ROTATOR CUFF TEAR
Subacromial impingement is a shoulder condition that involves pain above and anterior to the stump of the shoulder with a pinching sensation, which occurs mainly between 70° and 90° of abduction.
Subacromial conflict corresponds to a tendino-bursitis (tendinitis) of the tendons of the humerus cuff muscles that are compressed between the upper end of the humerus (greater tuberosity and humeral head) on one side and the acromion and acromiocoracoid ligament (ACL) on the other side.
Anatomical and pathological aspects of subacromial conflict
This pathology corresponds anatomically to tendinitis of the supraspinatus muscle tendon and inflammation of the subacromial bursa. This pathology, classified as a "conflict" condition, is exacerbated by a narrowing of the subacromial space by three anatomical structures:
- The acromion, which may be abnormally curved, hook-shaped
- El ligamento coracoacromial, que puede calcificarse con la edad
- The acromioclavicular joint, which can become thickened due to osteoarthritis
When shoulder calcifications are present, they contribute to both subacromial impingement and shoulder pain. A morphological abnormality called acromial bone may exist. It corresponds to a fusion defect of the acromion growth cartilages. When the acromial bone is pre-acromial or meso-acromial, it narrows the subacromial space and contributes to subacromial impingement.
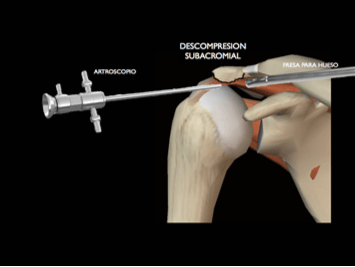
Surgical treatment of subacromial conflict by arthroscopy
It is performed when medical treatment fails (infiltration with long-acting corticosteroids and shoulder re-education).
Arthroscopic surgery involves removing the anatomical factors causing pain and discomfort, in order to increase the space for the rotator cuff tendons, primarily the supraspinatus.
Four surgical procedures are performed to release the subacromial space: surgical resection of the subacromial bursa, resection of the acromiocoracoid ligament, acromioplasty, and cleaning of the acromioclavicular joint.
In some cases, the removal of calcifications and/or the acromial bone may be associated.
Recovery after surgery
After arthroscopically assisted surgery, loose immobilization will be recommended for 2 weeks. Specialized shoulder rehabilitation should begin immediately after surgery. Convalescence and full shoulder recovery take 4 to 6 months after surgery.
The amount of sick leave required after surgery will depend on the type of work you do. For example, a one-month sick leave if you work in a bureaucratic capacity or three or four months if your job is more physical.
This information is provided by specialized healthcare personnel for informational purposes only and does not replace medical advice.
If you would like to make an appointment with our shoulder specialist in Bilbao, you can contact us by phone at 946 941 347 or by using the following form.